Mastering SharePoint document libraries is key to unlocking their full potential as one of the platform’s most powerful tools. Think of a document library as a digital filing cabinet designed to store, organise, and manage your organisation’s documents. But it’s much more than just storage—it offers robust features to streamline collaboration, ensure compliance, and guide your documents through their entire lifecycle.
When set up correctly, a document library becomes the cornerstone of efficient data management, ensuring documents are easy to create, collaborate on, approve, publish, archive, and ultimately delete when no longer needed. Let’s explore how document libraries work and how their features align with managing the document lifecycle.
Key Uses of a Document Library
1. Centralised Storage
A document library provides a single location for storing documents, ensuring your team has access to the latest versions of files anytime, anywhere. This eliminates confusion caused by scattered files across email, local drives, or multiple platforms.
2. Collaboration
SharePoint’s integration with Microsoft 365 allows teams to work on the same document simultaneously using apps like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint. Comments, real-time edits, and version tracking make collaboration seamless.
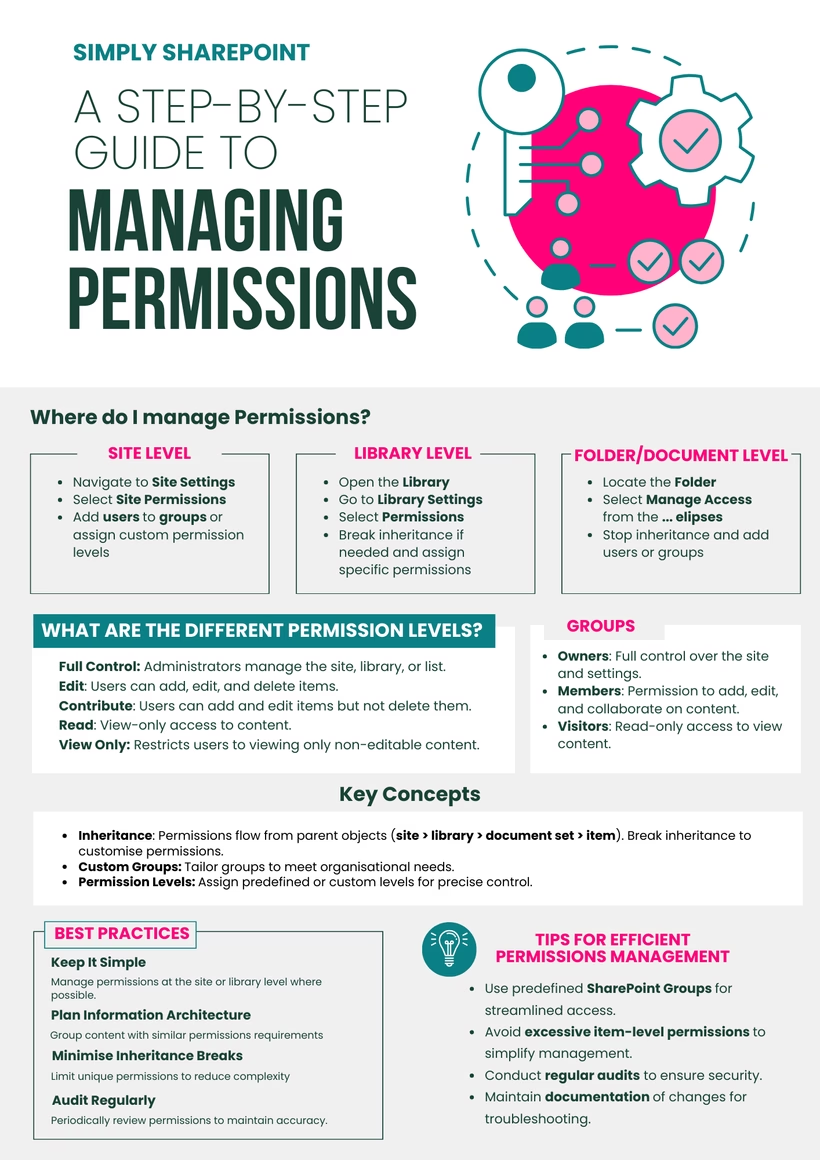
3. Compliance and Security
Document libraries enforce permissions, retention policies, and audit trails, helping organisations comply with regulations and protect sensitive information.
4. Workflow Automation
Automated workflows streamline processes like document approval, reminders for reviews, or task delegation, ensuring consistency and efficiency.
Document Lifecycle in SharePoint
A document’s lifecycle comprises several stages—from creation to deletion. Here’s how a SharePoint document library supports each stage:
1. Document Creation
Feature: Document Templates
Document libraries allow you to create templates for common document types (e.g., policies, contracts, or forms). When users create a new document, they can choose a pre-configured template, ensuring consistency and saving time.
Steps to Set Up Templates:
- Navigate to the library settings.
- Upload or configure a document template.
- Users can now create documents directly from the “New” menu.
2. Collaboration and Editing
Features: Co-Authoring and Version History
- Co-Authoring: Multiple users can work on the same document simultaneously, seeing each other’s changes in real-time.
- Version History: Every change is tracked, allowing you to view or restore previous versions if needed.
Tips for Effective Collaboration:
- Ensure permissions are correctly set to allow editing.
- Use @mentions in comments to notify team members.
3. Approval Workflows
Feature: Power Automate Integration
Approval workflows ensure that a document is reviewed and approved before it’s finalised. SharePoint libraries integrate seamlessly with Power Automate, enabling workflows for:
- Routing documents to approvers.
- Sending notifications for pending approvals.
- Recording approvals in the document’s metadata.
Example Workflow: A policy document might require approval from HR, legal, and management before it’s published.
4. Publishing
Feature: Metadata and Views
Publishing involves making the document available to its intended audience. SharePoint’s metadata and custom views help:
- Categorise documents for easy discovery.
- Surface the most relevant documents using filters and sorting.
Set Up Metadata for Publishing:
- Add columns for status (e.g., Draft, Approved, Published).
- Use views to display only “Published” documents to end users.
5. Archiving
Feature: Retention Policies
Once a document is no longer actively used, it can be archived. Retention policies in SharePoint automatically move documents to an archive folder or library after a set period.
How to Configure Archiving:
- Set up retention labels in Microsoft Purview.
- Define policies based on document type or activity.
6. Deletion
Feature: Lifecycle Management
When a document reaches the end of its lifecycle, it can be deleted. SharePoint ensures that:
- Deleted items are moved to the Recycle Bin for a configurable period (default is 93 days).
- Records management policies prevent premature deletion.
Steps to Automate Deletion:
- Configure retention labels to delete documents after a set period (e.g., seven years for financial records).
- Use workflows to notify owners before deletion.
Conclusion
A SharePoint document library is more than just a storage tool; it’s a robust solution for managing documents throughout their lifecycle. By leveraging its features—templates, collaboration tools, workflows, and retention policies—organisations can ensure consistency, compliance, and efficiency in document management.